
Background
This project follows a specific support request made by the Ministry of Disaster Management and Relief (MoDMR) to the UN Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) and the UN Resident Coordinator’s Office (UNRCO) for a sub-national earthquake hazard and risk assessment in Bangladesh. The GEM Foundation has the role of technical expert lead of the project which will include the following activities:
Needs and Gaps Assessment
Technical Panel Formation and Initial Consultations
Seismic Hazard Mapping
Exposure Mapping
Seismic Vulnerability Assessment
Seismic Risk Mapping and Interpretation
Stakeholder Consultation and Validation
Preliminary Model Dissemination and Training Workshop
Funding and technical partner: UNDRR
Duration: 2023 - 2024


Objectives
The main objective of this project is to develop a detailed, open, sub-national earthquake risk model and evaluate seismic risk for Bangladesh at the zila and upazila levels. The complete risk model will comprise a probabilistic seismic hazard model, a building exposure model, and a seismic fragility and vulnerability model for the building stock of Bangladesh. Additionally, it includes critical scenarios for key cities, identified based on the results of the probabilistic risk assessment and in consultation with local stakeholders and experts, in a panel led by the Ministry of Disaster Management and Relief (MoDMR), and including representatives from the Ministry of Housing and Public Works, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics, Geological Survey of Bangladesh, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, and University of Dhaka.`
Collaborators
In collaboration with the GEM Foundation, the Technical Panel steering this seismic risk assessment initiative is a collaborative assembly of key stakeholders and experts. Led by the Additional Secretary of Bangladesh's Ministry of Disaster Management and Relief (MoDMR), it comprises representatives from vital entities, including the Department Of Disaster Management (DDM), the Fire Service and Civil Defence of Bangladesh, the Ministry of Housing & Public Works (MoHPW), and the Statistics and Informatics Division (SID) of the Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS).
In addition, the panel includes the participation of seasoned national experts specializing in seismic hazard and risk assessment from institutions such as the University of Dhaka (DU), Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET), and Jahangirnagar University (JU). Further enriching the panel's knowledge base are contributions from the Geological Survey of Bangladesh, the Centre for Urban Studies (CUS), and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), Bangladesh.)


Location
Bangladesh

Earthquake Hazard and Risk Assessment Results
This section summarises the various assessments conducted to understand the potential impact of earthquakes in Bangladesh. These assessments cover a range of factors, including the likelihood and severity of ground shaking, liquefaction potential, exposure of people and buildings, vulnerability of infrastructure, and the overall seismic risk posed to the country. The following list details the outputs generated from each assessment.
Bangladesh Profiles | Past Earthquakes
**ALL RESULTS ARE PRELIMINARY AND UNDER REVIEW**
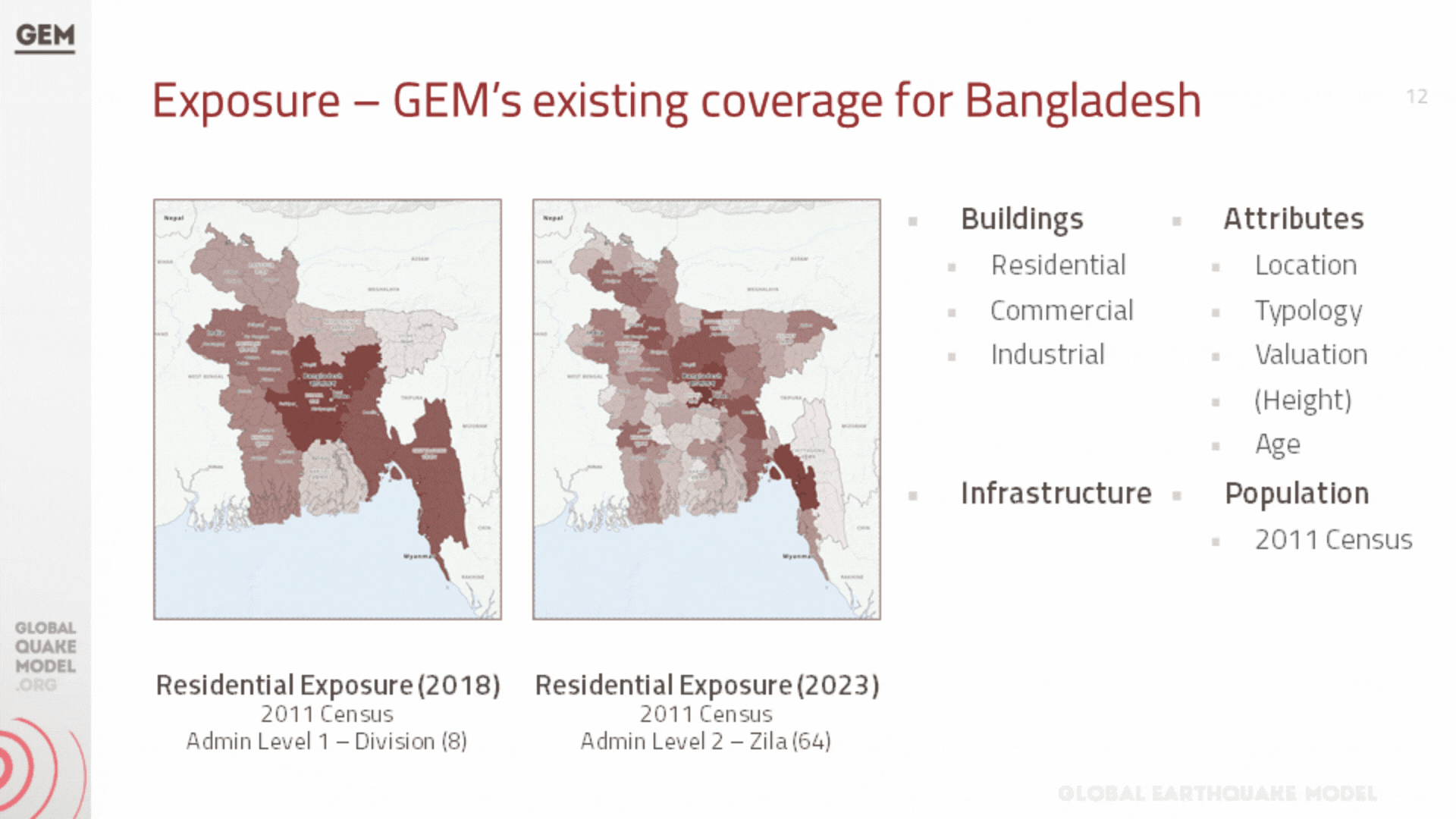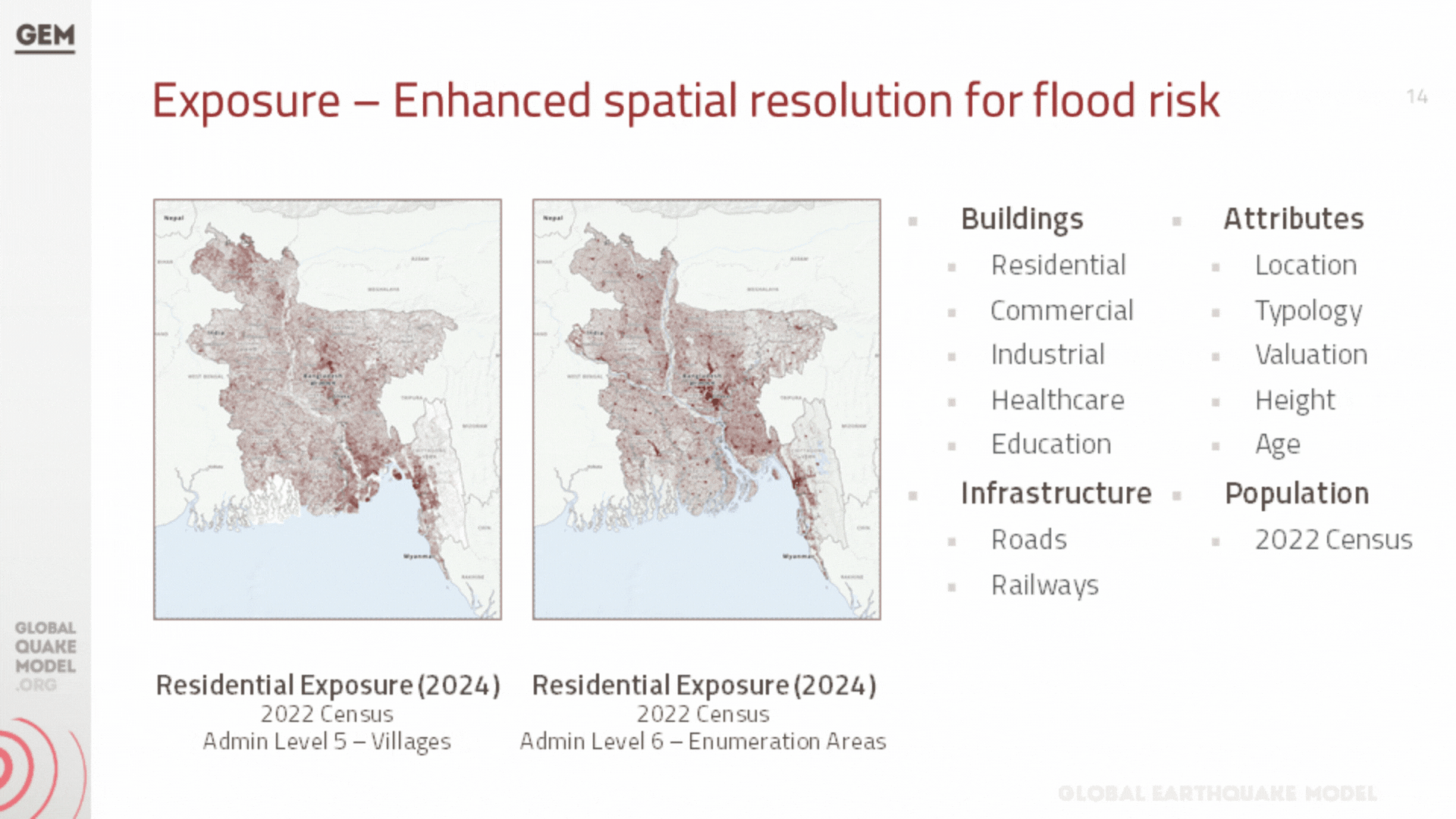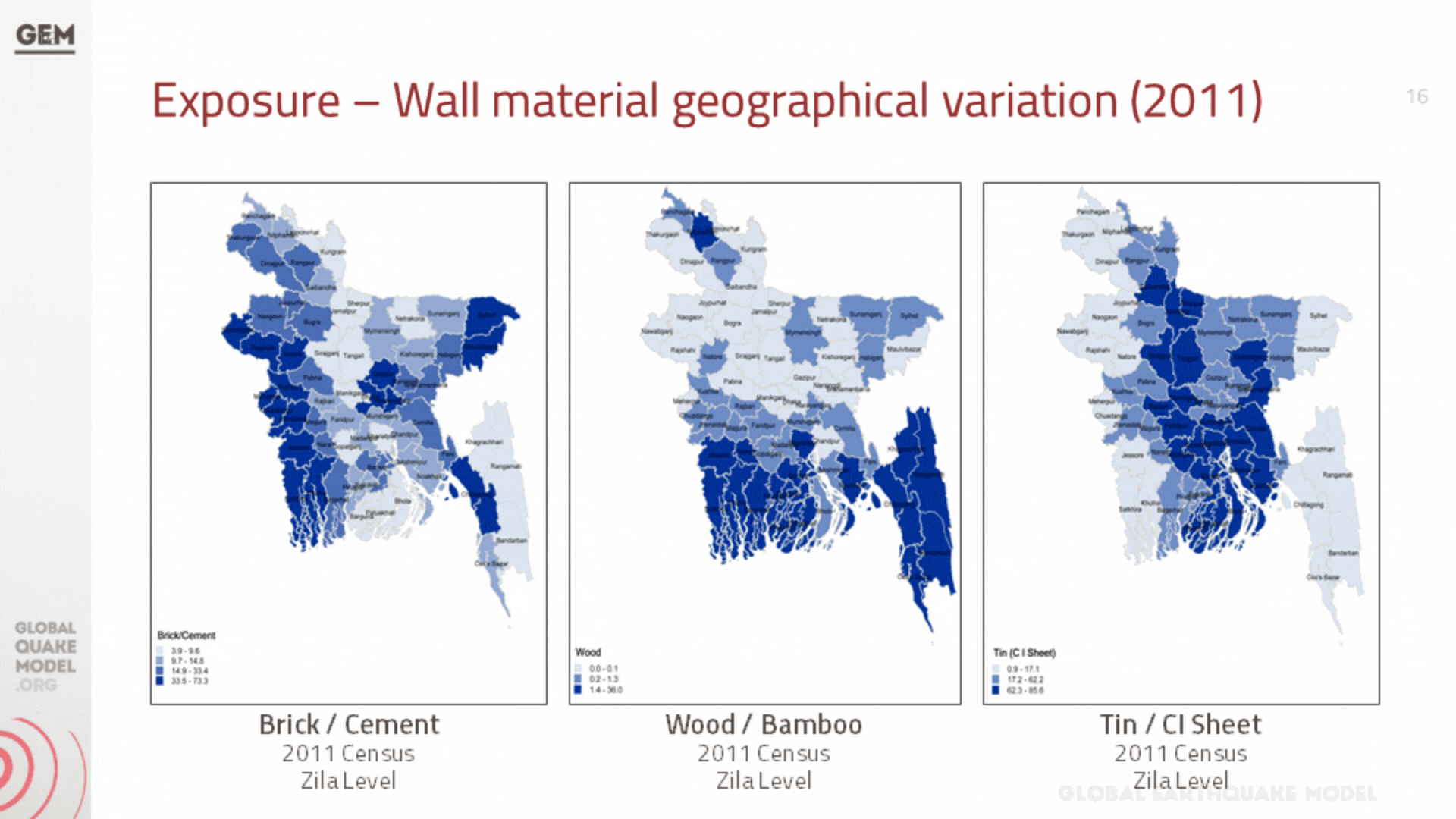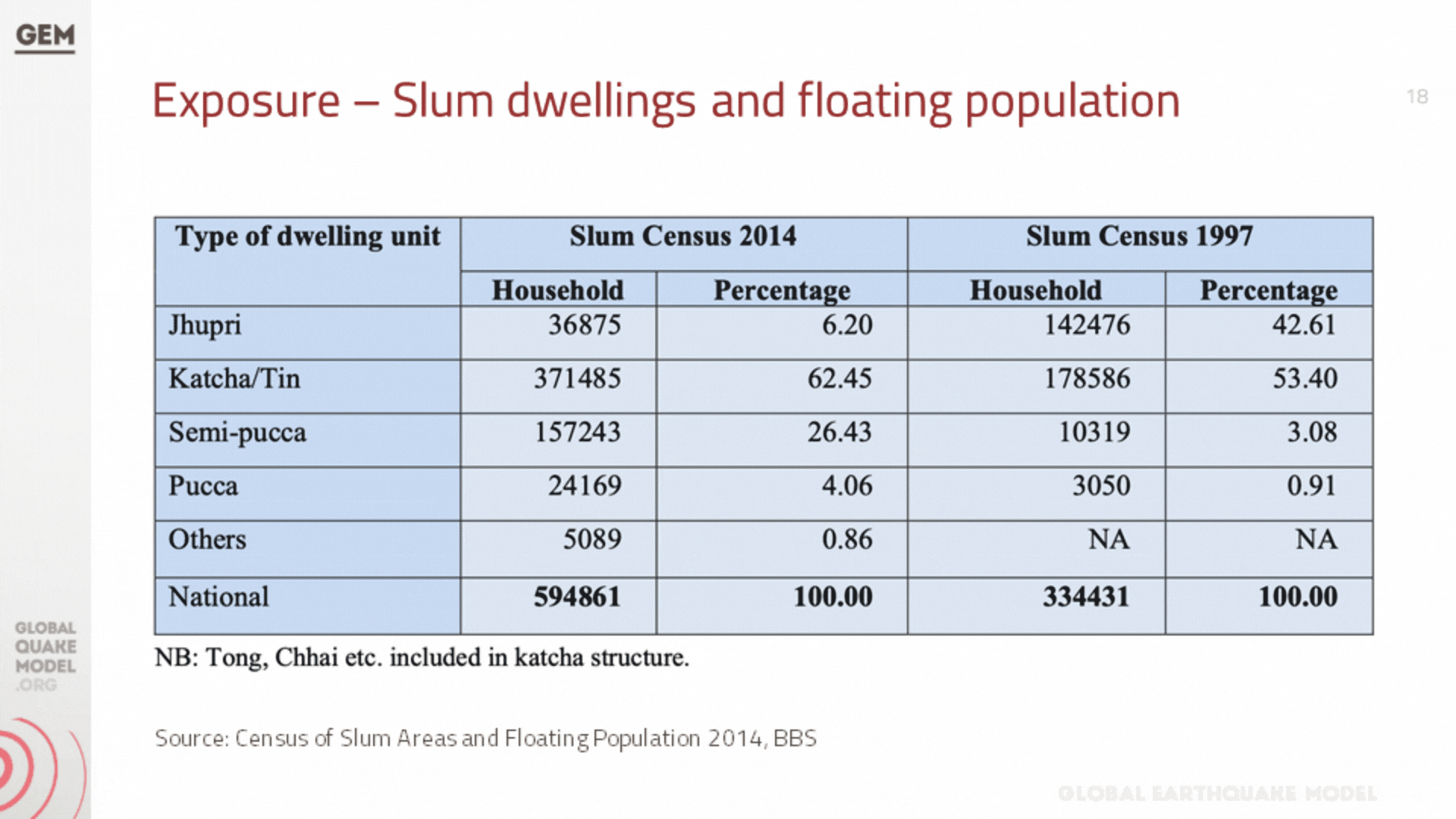
a. Population and Building Exposure
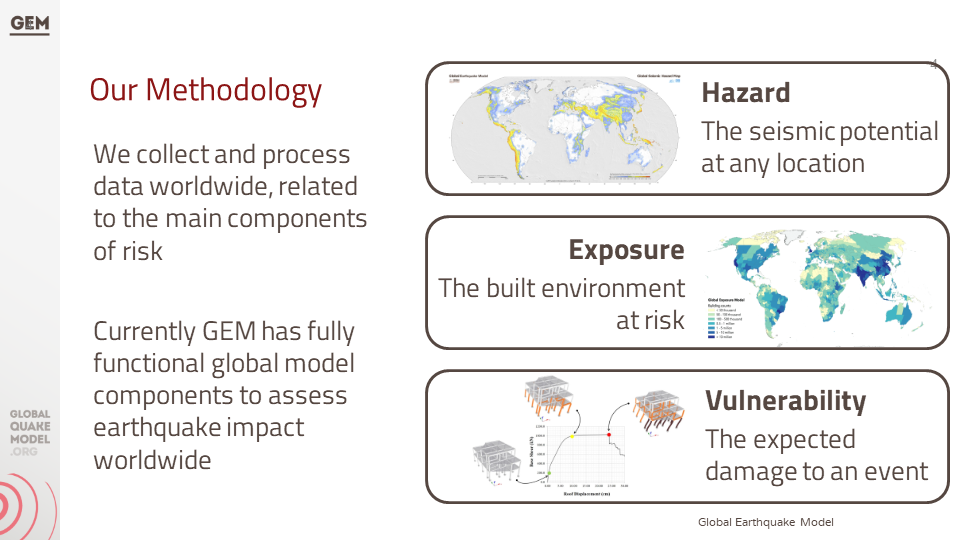
Exposure models play a critical role in seismic risk assessment by quantifying the potential exposure of buildings and infrastructure to earthquake hazards. These models are structured databases that catalogue the characteristics of buildings within a specific geographic area, including their location, construction material, age, occupancy type, and structural design. The depth and accuracy of this data directly influence the effectiveness of the seismic risk evaluations, as they allow for a detailed understanding of how different structures are likely to perform during an earthquake.
Download Files
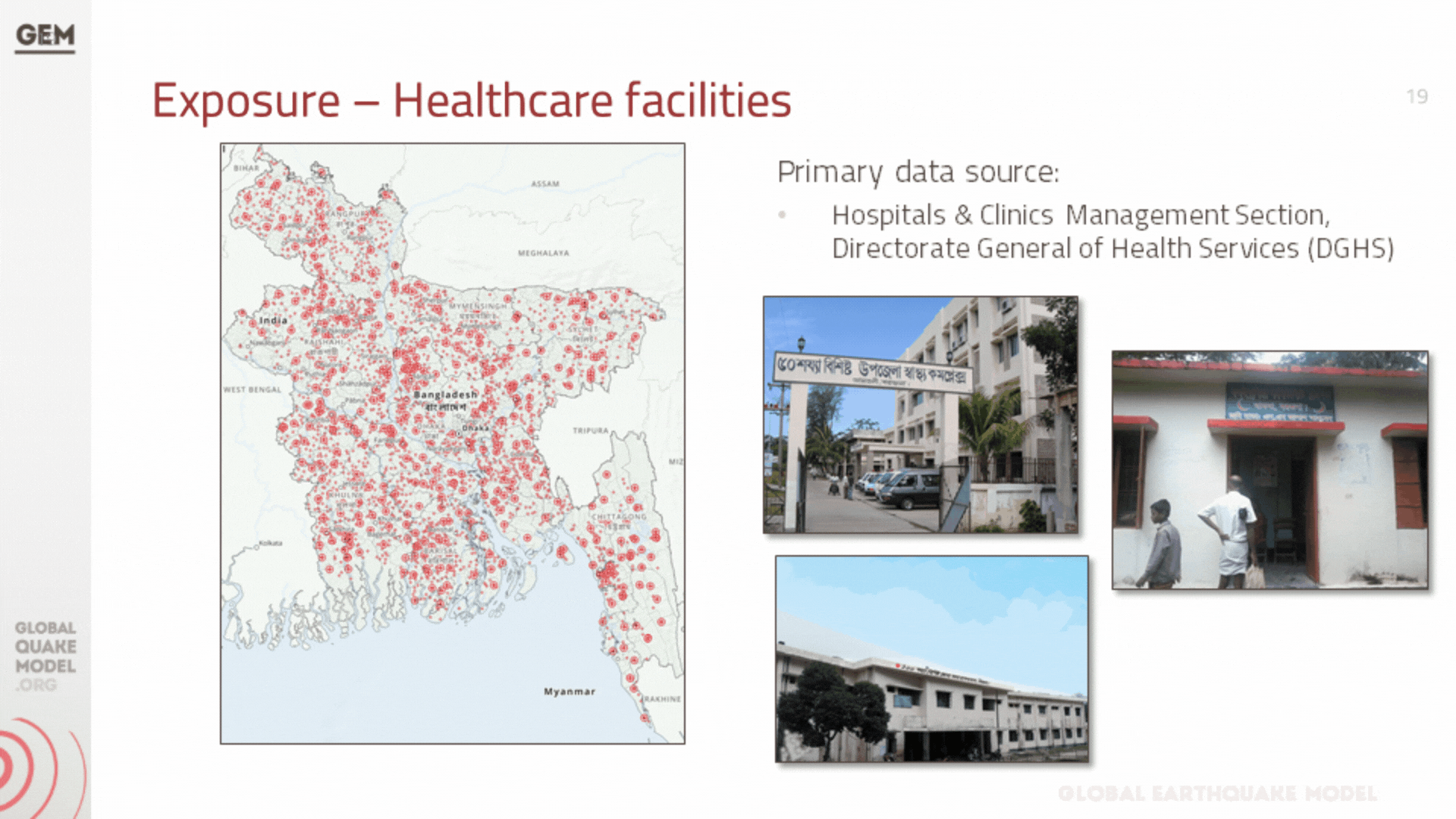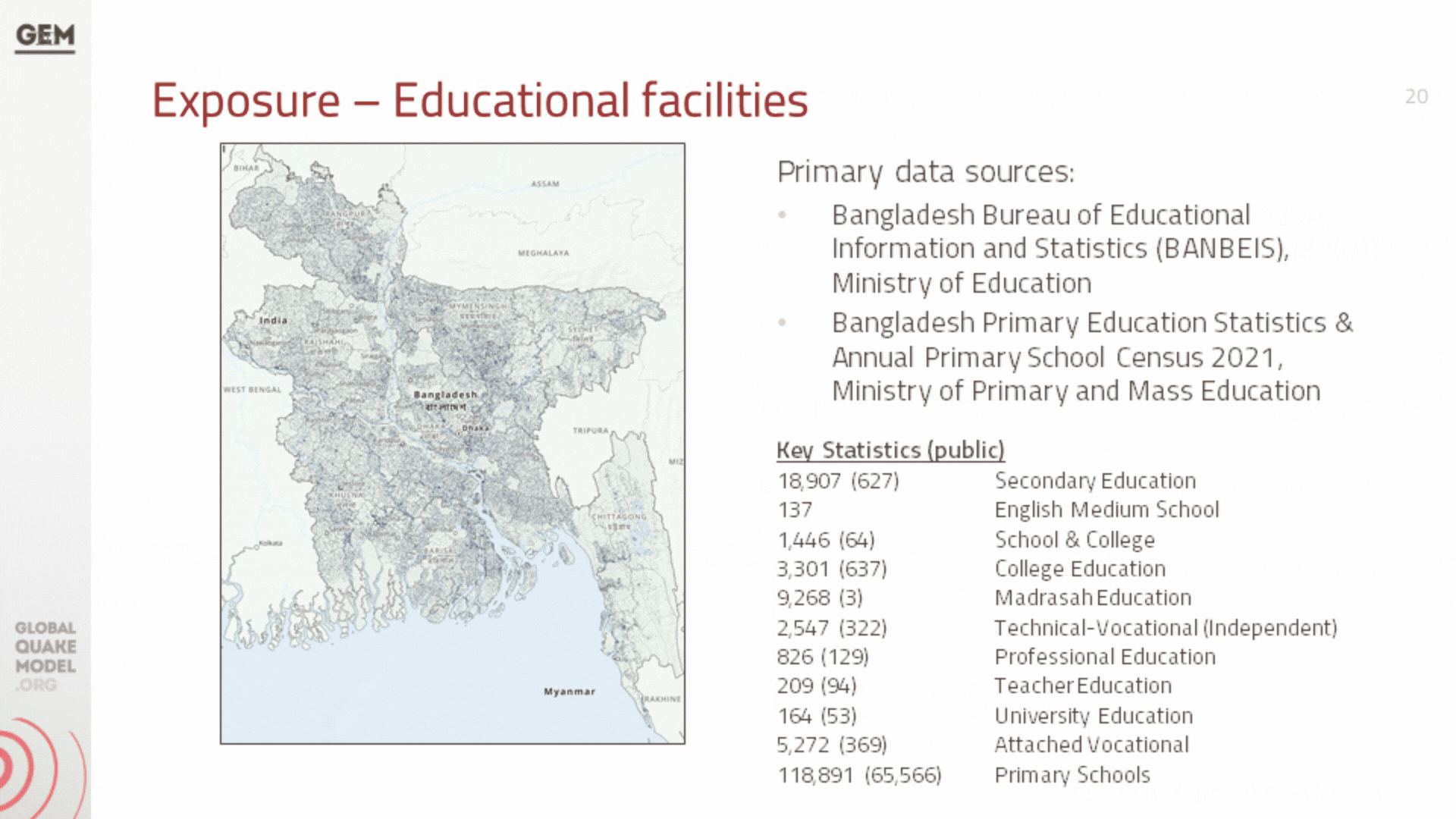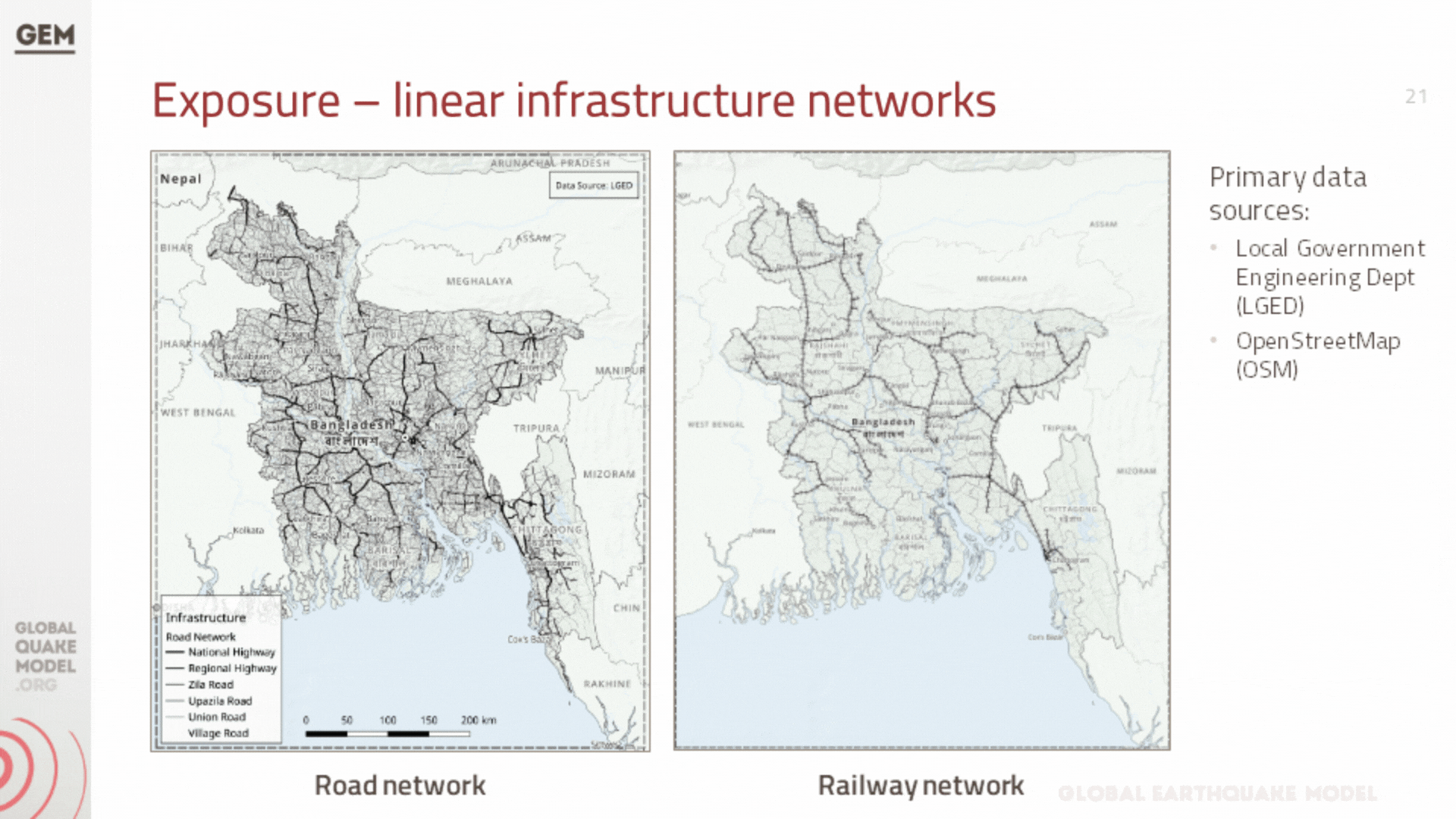
b. Infrastructure Exposure
In addition to residential, industrial, and commercial structures that were previously covered by GEM’s exposure models at the zila level (which have been updated to the upazila level during this project), we have also developed exposure models for the healthcare and educational facilities at the country, including all hospitals and clinics, and all schools, colleges, and universities.
c. Earthquake Scenarios
The project also constructed the rupture geometries for these events, selected a range of ground motion models, and assessed the potential impact—both in terms of damage and losses—that each event could inflict on the country if it were to occur today. The full scenario set consists of twelve events: seven historical events from 1664-1918, chosen out of many in this period, supplemented by five hypothetical events.
Download Files
d. Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Assessment
The seismic hazard modelling and mapping section describes the approach taken to assess the seismic hazard in Bangladesh with the goal of creating a comprehensive seismic hazard model for Bangladesh that can be used for risk assessment and mitigation. The project started with a probabilistic seismic hazard model for the Indian subcontinent, which was updated and implemented for the OpenQuake engine. The model includes seismogenic source models, ground motion models, and considers various tectonic regions. This section also mentions the review of the seismic source model for northeast India and the improvements made to the model.
Download Files
e. Liquefaction Hazard Assessment
The section "Liquefaction susceptibility and hazard assessment" discusses the inclusion of regional liquefaction occurrence models in the project, which predict ground failure using existing mapped information and above-ground inferences of below-ground conditions. These models were used for the national scale liquefaction hazard assessment in the second phase of the project identifying the factors that contribute to liquefaction, the methods used for assessment, and the potential damage and losses that can result from liquefaction.
Download Files
f. Seismic Risk Assessment
The project estimated seismic risk metrics utilising the OpenQuake-engine's stochastic event-based risk assessment calculator. A probabilistic seismic hazard analysis model was employed to generate earthquake rupture forecasts, forming a stochastic event set over a 100,000-year span. Economic and human losses were computed for each event, producing event loss tables and year loss tables. Risk metrics included exceedance probability curves and average annualized losses. Fatality and injury estimates relied on vulnerability models informed by global earthquake data, with a focus on South Asian building characteristics. Results were tabulated nationally and regionally by the project. The assessment also considers the exposure and risk of healthcare facilities, educational facilities, and the national road network to seismic hazards.
Download Files

Improving global capacity for seismic hazard and risk
This part of the program was designed to improve the understanding and awareness of earthquake hazard and risk, and to help bridge the gap between the information produced in detailed hazard and risk assessment studies and its communication to a wide variety of stakeholders (which range from local experts with the remit to assess seismic risk to decision-makers responsible for the implementation of risk reduction measures).

a. Website for OpenQuake online training
The OpenQuake online training was designed for different types of audiences with diverse backgrounds and expertise. Through this platform, participants interact with GEM scientific and technical teams to learn the main concepts of earthquake risk assessment, along with the basic features of the engine.
[English]

b. Onsite Training Workshop
One-day workshop designed to improve the understanding and awareness of earthquake hazard and risk and to help bridge the gap between the information produced in the project and its communication to a wide variety of stakeholders.
The session allowed participants to explore and prepare the required input files for earthquake scenarios in the OpenQuake engine.
OQ Engine Video Tutorials | English | Example Material

Communicating and raising earthquake risk awareness
The activities in this component focused on raising the awareness of the public on earthquake hazard and risk by training a diverse group of disaster risk reduction (DRR) professionals together with personnel in charge of communicating risk to the public, and by conducting community-based workshops in selected areas of the pilot cities by those who were trained by the project.

Speech by Domenico Scalpelli (WFP Representative) on the presentation of the Earthquake Risk Assessment Results
The speech was delivered on March 6, 2024 at Six Season Hotel, Hall Room, Bunka, Bangladesh (10:00 am to 12:30 pm).
"While Bangladesh has been fortunate to avoid a significant earthquake in the past century, historical data suggests earthquakes are a threat. This analysis, considering hazard, exposure, and vulnerability, provides a foundation for evidence-based decision-making to guide preventive measures, enhance preparedness, and fortify our ability to respond."
a. GEM presentation to the Ministry of Disaster Management and Relief (MoDMR), Bangladesh
This is an introductory presentation on Bangladesh's earthquake risk assessment project that outlines past efforts, emphasises the need for a nationwide evaluation, and introduces the GEM Foundation's methodology. It highlights completed division-level risk maps and ongoing project activities like data collection, vulnerability assessment, and stakeholder engagement.
Additionally, five other presentations below will address different aspects of the project in Bangladesh.
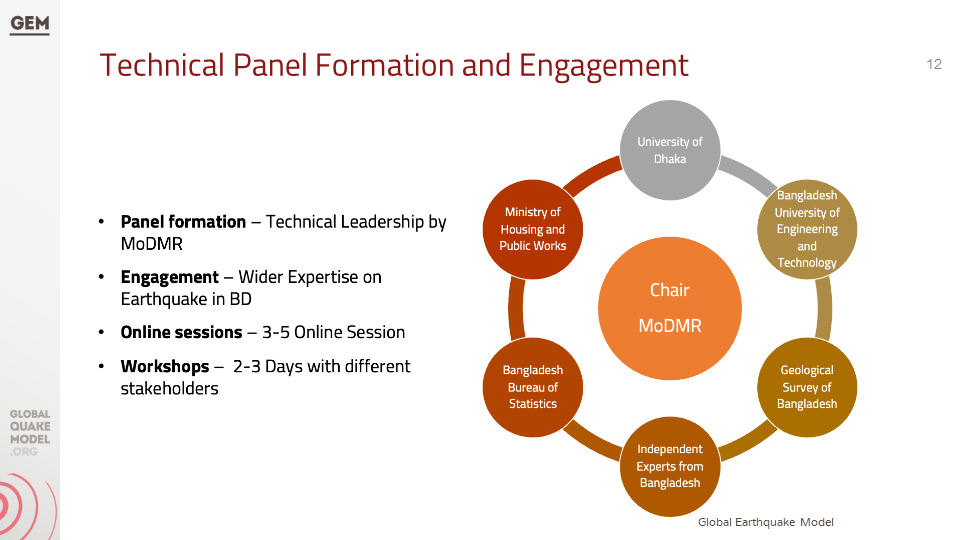
b. Technical Panel Session #1
This presentation discusses the methodology used to collect and process data related to earthquake risk components such as hazard, exposure, and vulnerability. It also mentions the project activities and the formation of a technical panel for consultation and validation.
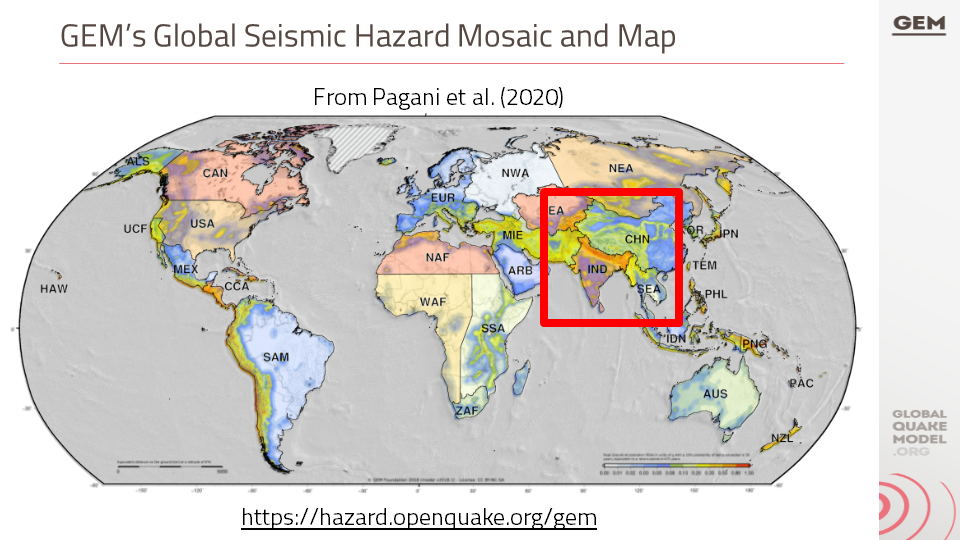
c. Technical Panel Session (PSHA) #2
This presentation is about the tailored version of the PSHA (Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Assessment) model for the Indian sub-continent, which is based on the original model developed by Nath and Thingbaijam in 2012. The presentation discusses the main areas identified for improvement in the model, the changes that were introduced, and the impact of these changes on the hazard results.
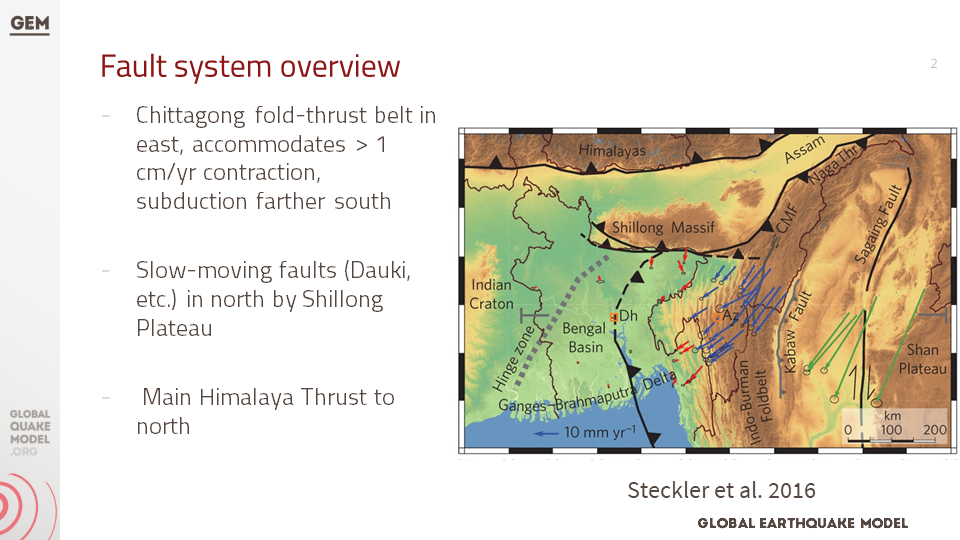
d. Technical Panel Session (Scenario Ruptures) #2
This presentation is about the hazard analysis of earthquakes in Bangladesh, including an overview of the fault systems, historical ruptures, and potential ruptures. It also mentions the ground motion models used for the analysis.

e. Technical Panel Session #3
This presentation focuses on exposure and physical and social vulnerability, as components of seismic risk. It discusses the details of exposure models, seismic vulnerability analysis, and social vulnerability. The presentation also mentions the use of the Global Earthquake Model (GEM) and the INFORM Index in assessing and understanding the seismic risk in Bangladesh.
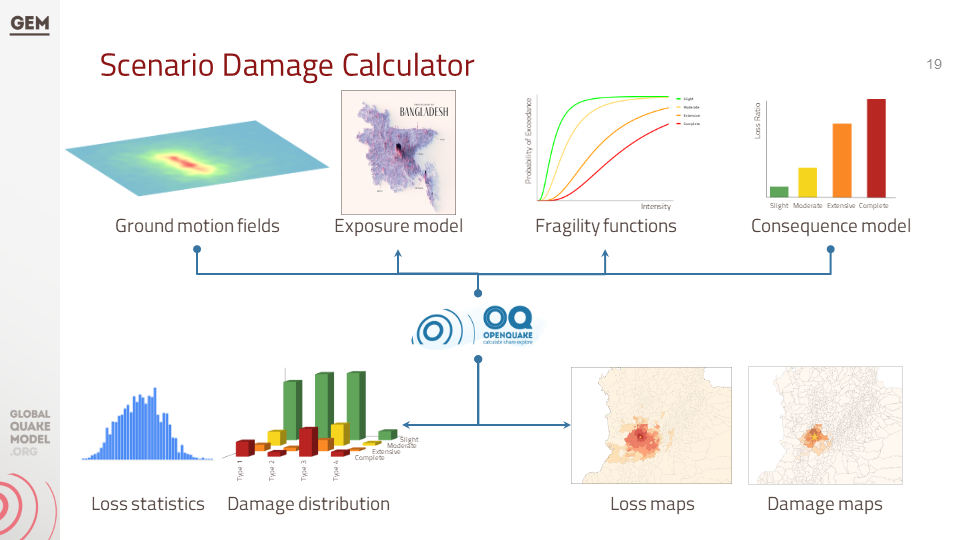
f. Technical Panel Session (Scenarios and Risk) #4
This presentation details data collection and processing methods for seismic hazards, exposure, and vulnerability. It presents preliminary results on potential earthquake impacts like building collapse and economic loss using an 1885 event as an example. The presentation also mentions probabilistic risk assessment and division-level risk maps, alongside details about 12 "scenario ruptures" based on historical and potential earthquake events.
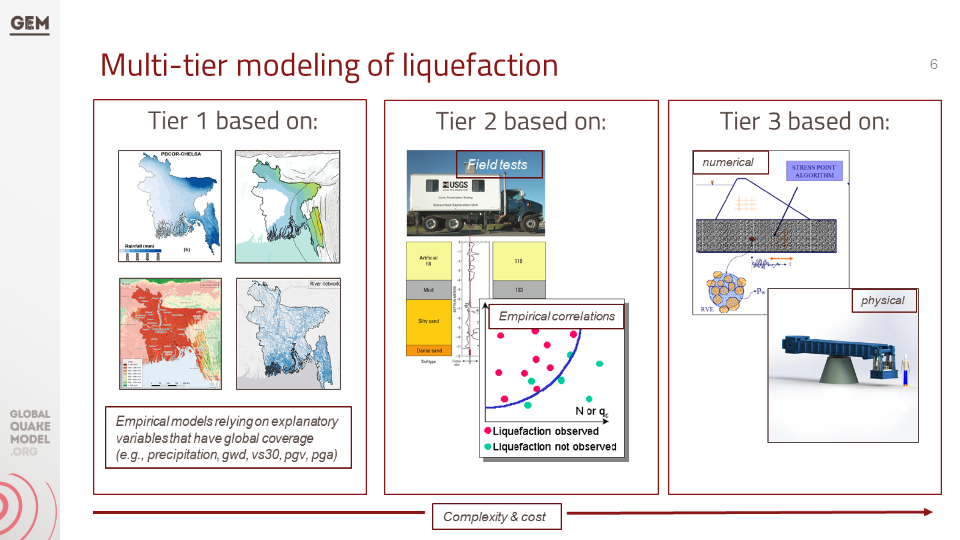
g. Technical Panel Session (Liquefaction) #4
This presentation focuses on factors such as soil liquefaction, susceptibility to ground failure, population density, urbanisation, and the country's river delta geography. It discusses various methodologies and models used to assess liquefaction hazard and suggests the use of geospatial methodologies for identifying areas with a higher likelihood of occurrence.

h. Final UNDRR-GEM Bangladesh - MoDMR Presentation
This presentation summarises the findings of a sub-national earthquake hazard and risk assessment for Bangladesh, conducted by the Global Earthquake Model (GEM) Foundation in collaboration with MoDMR, UNDRR and UNRCO.
It details the development of a comprehensive earthquake risk model for Bangladesh at the district and sub-district levels. The presentation covers the methodologies employed, including assessments of seismic hazard, exposure, and vulnerability. Stakeholder engagement and the final earthquake risk model for Bangladesh are also presented.

Videos - Ruptures, PSHA and Liquefaction
The Global Earthquake Model (GEM) Foundation presents insights into the Bangladesh earthquake risk assessment project. These presentations will explore scenario earthquakes, a customized seismic hazard model, and the assessment of earthquake-induced liquefaction hazards.

1. Scenario earthquakes for Bangladesh hazard and risk analysis by Richard Styron
This presentation explores the concept of scenario earthquakes and their role in analysing earthquake hazards and risks in Bangladesh. Richard Styron will discuss the specific scenarios considered for Bangladesh, providing insights for understanding potential earthquake impacts.

2. PSHA Model for Indian sub-continent: tailored version of Nath and Thingbaijam (2012) by Kendra Johnson
Kendra Johnson will present a tailored version of the PSHA (Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Assessment) model developed by Nath and Thingbaijam (2012) for the Indian subcontinent. This presentation will explain how this model has been adapted to provide a more accurate assessment of earthquake hazards specific to Bangladesh.

3. Earthquake-induced liquefaction hazard assessment: scenario and probabilistic analysis by Lana Todorovic
This presentation by Lana Todorovic focuses on earthquake-induced liquefaction, a major concern in Bangladesh due to its river delta geography. Lana will discuss both scenario-based and probabilistic approaches to assessing liquefaction hazard, providing valuable information for mitigating this specific earthquake risk.
BUSINESS NEWS
March 6 presentation Humanitarian Organisations






BUSINESS NEWS
March 5 OpenQuake Training






BUSINESS NEWS
March 4 presentation




BUSINESS NEWS
March 3 meeting with MoDRM






BUSINESS NEWS
Images from online meetings: September to December 2023







Interim Substantive Reports
The documents below are interim substantive reports on the project "Earthquake Vulnerability and Systemic Risk Assessment in Bangladesh". The main objective of the project is to develop a detailed earthquake risk model for Bangladesh at the zila and upazila levels. They describe the development of an open-source probabilistic seismic risk model for Bangladesh and provide key insights to decision-makers and stakeholders in the disaster risk mitigation community.
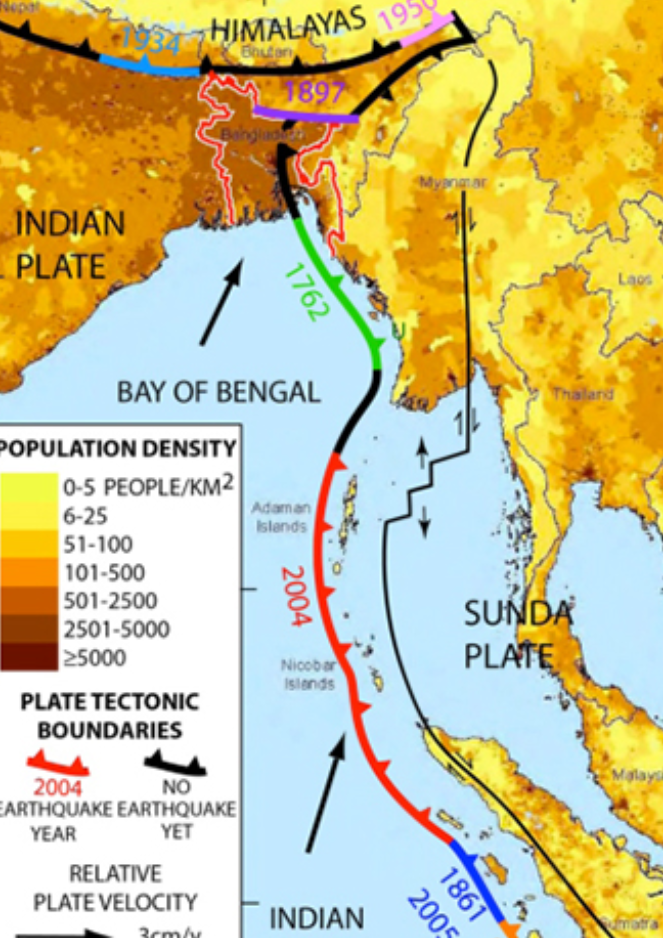
a. First Interim Substantive Report
This report highlights the need for a seismic risk model in the country and discusses the gaps and needs assessment. The report also explains the technical approach and methodology for developing the risk model, including seismic hazard modeling, liquefaction susceptibility and hazard assessment, exposure modeling, and seismic fragility and vulnerability modeling. The seismic risk assessment process is described, along with the formation of a technical panel and stakeholder engagement.
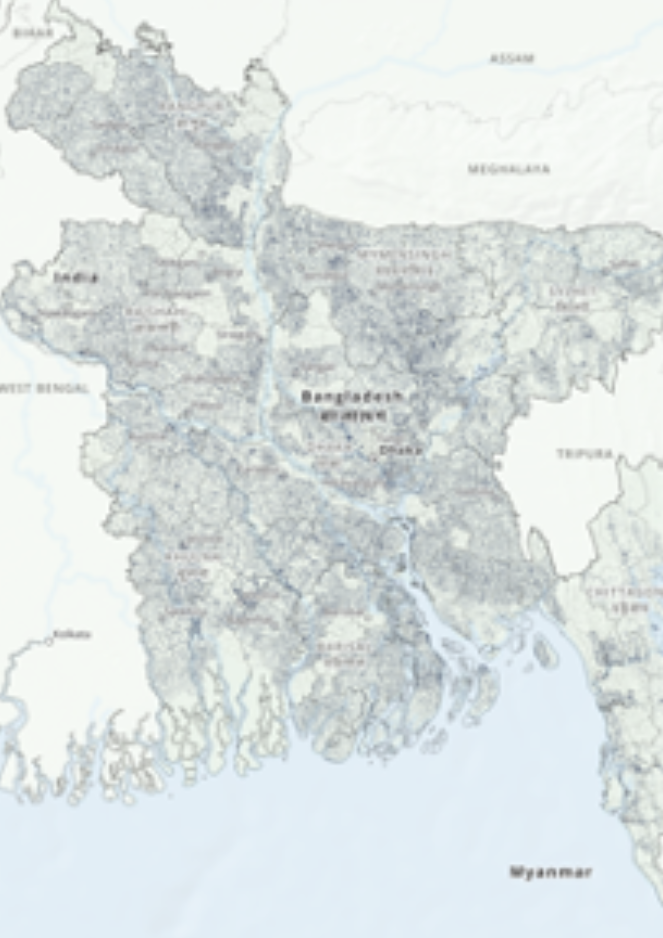
b. Second Interim Substantive Report
This report provides updates on various aspects of the project, including the development of earthquake scenarios, liquefaction susceptibility and hazard assessment, exposure modeling, and social vulnerability modeling. The report mentions that the project has engaged a technical panel comprising key experts and stakeholders, and their feedback and suggestions are being incorporated into the project. The report also includes information on the distribution of hospitals, clinics, schools, and colleges in Bangladesh.

c. Final Report
This report details the findings of a sub-national earthquake hazard and risk assessment for Bangladesh, undertaken by the Global Earthquake Model (GEM) Foundation. The project fulfills a specific request from the Ministry of Disaster Management and Relief (MoDMR) to the UN Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) and the UN Resident Coordinator's Office (UNRCO).
The project aimed to develop a comprehensive earthquake risk model for Bangladesh at the district and subdistrict levels. This report details the activities undertaken, including needs assessment, technical consultations, hazard and exposure mapping, vulnerability assessment, risk analysis, stakeholder engagement, and final model dissemination.
This assessment provides Bangladesh with crucial data to guide earthquake risk reduction efforts nationwide.


