QUICK LINKS
PROFILES
PUBLICATIONS
EXPOSURE
VULNERABILTY
SOFTWARE
EQ MODELS
Search Results
537 items found for ""
- GFDRR-DFID | Global Earthquake Model Foundation
Projects GFDRR-DFID GFDRR-DFID Challenge Funds Versión en español English version Share Facebook X (Twitter) LinkedIn Overview Background The Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery (GFDRR) and the UK Department for International Development's (DFID) competitive Challenge Fund pilots new and innovative approaches to overcoming technical and technological challenges in order to strengthen disaster and climate risk decision-making in developing countries. To this end, this project is supporting the development of data, products, and approaches to support disaster risk management decision-making and build resilience, including through better information, but also strengthening key steps in moving from information to insight and behaviour change. Each challenge is focusing on the development of a database with hazard footprints, exposure information and vulnerability models. The viability of the databases will be demonstrated using exposure data for Tanzania and another DFID priority country. Objectives The project is divided into three components. The British Geological Survey leads the development of a data schema and data for a multi-hazard database (Challenge 1) while GEM and University College London lead the development of a global exposure database (Challenge 2) and open vulnerability platform for evaluating risk (Challenge 3) respectively. GEM also contributes to Challenge Fund 1 and 3. GEM leads Challenge Fund 2 on the development of a global exposure data framework, which includes the physical vulnerability characteristics and exposure taxonomy. The aim is to identify the most important vulnerability characteristics; ways to account for uncertainties in exposure and vulnerability models; type of assets that should be supported by the vulnerability and exposure database; and the most common and useful intensity measure types. The objective of this project is to develop a Data Exploration Tool to promote the ability of a user to access, understand and use hazard, exposure and vulnerability data stored in a format that follows the data schema developed by the Challenge Fund consortia. British Geological Survey (BGS) leads the development of a data schema and data for a multi-hazard database (Challenge 1) GEM Foundation leads the development of a global exposure database (Challenge 2) University College London (UCL) leads the development of open vulnerability platform for evaluating risk (Challenge 3) Various organizations also participated and contributed to the project such as the Geological Survey of Tanzania; Ardhi University (Tanzania); Dar Es Salaam University (Tanzania); DFID Tanzania; Prime Minister's Office - Disaster Management Department (Tanzania); DoMA (Malawi); INGC (Mozambique); Ministry of Energy & Mineral Development (Uganda); ImageCat (USA); Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team (HOT Indonesia); NSET (Nepal); IDF (Switzerland); UA (Netherlands); NGI (Norway); NOC (UK); CIMA (Italy); and UCL-EPI (UK). Locations Tanzania and neighbouring countries A consortium led by the GEM Foundation with partners ImageCat Inc. and the Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team completed recently an open exposure database for multi-hazard risk assessment... The University College London (UCL) EPICentre and CatLin XL hosted the second workshop held on July 27 in London to collect feedback. The GFDRR-DFID Challenge Fund projects on the development of exposure, vulnerability and hazard footprints databases kicked off with a 2-day inception workshop. GFDRR-DFID Challenge Funds Round 2 How can innovative approaches make communities more resilient to climate change and natural disasters? GFDRR-UK Aid Challenge Fund: Final Learning Report: Value of Risk Information for Decision Making May 31, 2018 Data schema and data: for multi-hazard database (BGS), for global exposure database (GEM), for a global database of vulnerability functions (UCL) Extensible Data Schemas for Multiple Hazards, Exposure and Vulnerability Data published as part of the UNDRR GAR2019 .
- SARA Project | Global Earthquake Model Foundation
Projects SARA Project South American Risk Assessment (SARA) Versión en español English version Share Facebook X (Twitter) LinkedIn Overview Outcomes Training Outreach Photos Publications Overview South America incorporates some of the most seismically active regions on the planet, where the South American subduction zone generates the forces to create the Andes Mountains and drives the occurrence of destructive earthquakes across Chile, western Argentina, Bolivia, Ecuador, Peru, Colombia and Venezuela. In turn, the high vulnerability of many structures and the high population density of the main cities are factors that contribute to the region’s high seismic risk. In the last two decades alone, over 3,000 fatalities have been reported, and the economic losses have exceeded 30 billion USD (EM-DAT, www.emdat.be ). While expert capabilities exist in these countries to assess earthquake risk, the information, infrastructure, tools, and collaboration networks necessary to develop comprehensive knowledge among scientists and engineers and to move this knowledge into the mainstream of disaster risk reduction activities has been lacking. Objectives The approach is to bring together international best practice tools and methodologies with local expertise and knowledge needed to establish local ownership and define risk assessment objectives and priorities. GEM Foundation combined these elements and focused on developing local capacities across sectors (academic, public and private), across technical disciplines (e.g., hazard, risk, IT), and through the implementation of disaster risk reduction policies and programs. The program of capacity development was initiated in 2013 with the South America Risk Assessment (SARA) Project to bring experts, institutions, and stakeholders from 7 countries to develop a regional assessment of earthquake hazard and risk. GEM provided its OpenQuake earthquake hazard and risk analysis software and other tools and databases freely and openly to all participants. More than 50 of the region’s experts across 17 institutions collaborated to produce critical data sets, develop common approaches, and develop open-source tools for both data collection and interpretation. Collaborators The SARA Project, completed in December 2015, provided the foundation for formal and informal collaborations at many levels and for many purposes. GEM subsequently developed formal partnerships across public and private sectors (e.g., SuraAmerica Insurance, the Geological Survey of Colombia, EcoPetrol), academic partnerships (e.g., EAFIT Univ, Univ del Norte, Univ Catolica Chile), non-profits (e.g., OSSO), and most recently, with municipal governments (Cali, Colombia and Quito, Ecuador), for urban risk assessments. (complete list ) Location Andean Region (Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile and Argentina) Introduction The project was carried out by experts and institutions from the region using to the extent possible open data sets, methodologies and tools such as GEM’s new open source software, the OpenQuake Engine and other OpenQuake tools. The project revolved around 5 modules: hazard, exposure and physical vulnerability, socio-economic vulnerability and resilience, loss estimates and city scenarios. The modules were carried out by a variety of experts/scientists from the region , in collaboration with the project coordinators and, where relevant, the GEM Secretariat. 1. Seismic hazard In early 2013 the Global Earthquake Model (GEM) published seven Requests for Proposal covering topics related to the compilation of basic datasets as well as the creation and calculation of an updated probabilistic seismic hazard input model for South America. Five consortia of South American researchers responded to this request and submitted proposals, which were reviewed in an initial stage by scientists working at the GEM Secretariat, and successively discussed in a meeting in Bogota held in December 2013 at the “Servicio Geologico Colombiano”. 2. Exposure and Physical Vulnerability Development of exposure datasets and vulnerability functions for South America at regional, national and/or sub-national levels have been considered. Modelling of exposure and physical vulnerability in the most earthquake prone countries is the main goal in the first stage of the project. 3. Social Vulnerability and Resilience The social vulnerability component of SARA comprises the development of composite indicators of social vulnerability and resilience along with their robustness testing and validation. The objective is to provide tools and information useful for understanding the potential effects of earthquakes in communities of South America. 4. National and subnational estimation of losses An open and transparent seismic risk assessment for the Andean countries has been performed. A probabilistic approach was followed for the calculation of risk metrics, that includes average annual economic and human loss maps, mean loss exceedance curves per country, and statistics that reveal which building classes are most vulnerable to earthquakes. 5. City Scenarios Following the objectives of SARA, the development of city scenarios is crucial for planning risk management strategies in cities with larger concentration of population and exposed to significant hazard. In this sense, the GEM Secretariat has been seeking collaborations with research groups and governmental stakeholders that will be the end users of case studies in Lima (Peru), Quito (Ecuador), Medellín (Colombia), Iquique, Osorno and Rancagua (Chile). Capacity development and institutional strengthening To promote sustainability, SARA’s work included the following: capacity development and institutional strengthening, and stakeholder engagement. The outcomes of activities in these areas are described below. A blog by Carlos Costa featuring the SARA project workshop in Chile 2014. [News ] A wiki project website containing technical information about the SARA project. [Website ] BUSINESS NEWS Quito workshops 2015 1/3 BUSINESS NEWS Lima workshops 2015 1/2 SARA Project Executive Summary [PDF ] Probabilistic Seismic Risk Assessment Of The Residential Building Stock In South America [PDF ] A conference paper on Building A Ground-Motion Logic Tree For South America Within The Gem-Sara Project Framework [PDF ] SARA (South America Risk Assessment Project Workshop) on “Inventory of Quaternary deformation of South America” [PDF ]
- GEORGIA DRR | Global Earthquake Model Foundation
Projects GEORGIA DRR Capacity building to understand and take action on seismic risks in Georgia Versión en español English version Share Facebook X (Twitter) LinkedIn Overview Background This project aims to enhance the understanding of earthquake impacts in Georgia and to address the following two challenges: i. The lack of understanding of potential earthquake risk and the impact on people, infrastructure and the economy at large; and ii. the lack of efforts to reduce the vulnerability of existing infrastructure, particularly critical emergency response infrastructure. The project is divided into 5 tasks, with the GEM Risk Team contributing to all tasks, with a specific emphasis on developing exposure models, identifying vulnerability models and running the probabilistic seismic risk assessment with the OpenQuake engine: Task 1 – Project Inception Task 2 – Preparation of Input Data & Development of Input Models Task 3 – Seismic Risk Analysis Task 4 – Recommendations on Risk Reduction Strategy Task 5 – Capacity Building Workshops Duration: 2020-2021 Objectives The objective of this project is to provide greater insight to the World Bank into the exposure of Georgia’s emergency response sectors to earthquakes and the potential consequences, as well as strategies to build seismic resilience in these sectors. The findings allow the World Bank to develop recommendations and better advise the Government of Georgia on how to: i. enhance its capacity to plan for future risk reduction investment programs based on a better understanding of earthquake risk in emergency response buildings; ii. develop options for a framework for a future short, medium and long-term intervention strategy; and iii. communicate and build consensus on earthquake risks and potential interventions in key sectors. Collaborators GEM Foundation, Arup, Progress Project LLC, Ilia State University Funding partner: World Bank Group Location Georgia
- SSAHARA Project | Global Earthquake Model Foundation
Projects SSAHARA Project Sub Saharan Hazard and Risk Assessment (SSAHARA) Versión en español English version Share Facebook X (Twitter) LinkedIn Overview Outcomes Training Outreach Photos Publications Background The East African Rift System (EARS) is the major active tectonic feature of the Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) region. Although the seismicity level of such a divergent plate boundary can be described as moderate, several damaging earthquakes have been reported in historical times, and the seismic risk is exacerbated by the high vulnerability of the local buildings and structures. Formulation and enforcement of national seismic codes is therefore an essential risk mitigation strategy. A reliable risk assessment must be based on an updated and reliable seismic hazard model for the region. The last published regional model for SSA was developed within the frame of the GSHAP project and is almost 20 years old (Midzi et al., 1999). The availability of new data, local and regional seismotectonic studies and recently developed methods and tools prompt the development of a new PSHA model summarizing the current state of knowledge in Sub-Saharan Africa. Objectives In September 2014, the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) GEM funding support to implement a program entitled “Reducing Earthquake Risk collaboratively by Building Capacity and Leveraging GEM’s Open Tools and Resources”. One of the objectives of this program was: to build the capacity in sub-Saharan Africa for integrated risk assessment and development of city earthquake scenarios involving local decision-makers. The project produced the SSA-GEM homogenized catalogue; the Seismic Source Zones; the Probabilistic Hazard Calculations; the Strain Rate Model; earthquake risk in East Sub-Saharan Africa; the residential building stock; and the Social Vulnerability and Integrated Risk in Sub Sahara Africa. Collaborators The development of a regional model would not have been possible without the contribution of experts from the local scientific community. Partnership with local governmental institutions and authorities was an essential step to facilitate model acceptance and for potential integration with national seismic codes. GEM worked with the following institutions for the implementation of the SSAHARA project. African Union; AfricaArray; FEPRA – Ethiopia; University of Pennsylvania; Addis Ababa City Government; UNDP Regional Office; and international agencies, municipalities and government agencies Location Burundi, Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Rwanda, Tanzania, Uganda Website SSAHARA wiki website containing technical descriptions and overview of the project. News Preventionweb article on the release of the Africa Model developed as part of the Sub-Sahara Hazard and Risk Assessment (SSAHARA) project funded by USAID. Disclaimer The contents of this project website such as studies, reports, audio-visual, news articles, blogs, and other information or media products including those in the external links are made possible by the generous support of the American people through the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). The contents are the responsibility of the Global Earthquake Model (GEM) Foundation and do not necessarily reflect the views of USAID or the United States Government.
- BACK TO NORMAL | Global Earthquake Model Foundation
Projects BACK TO NORMAL Earthquake Recovery Modelling Versión en español English version Share Facebook X (Twitter) LinkedIn Overview Background To address some of the key factors that influence recovery following a potentially devastating earthquake, the Alfred E. Alquist Seismic Safety Commission (SSC) engaged the GEM (Global Earthquake Model) Foundation and the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA), Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, a) to develop a methodology and an open-source and transparent software tool to estimate recovery states and recovery times following an earthquake; and b) to investigate the effect of external socio-economic factors on these recovery times. Objectives This project achieved the following main objectives: 1. Development of a user-friendly, non-commercial and transparent software tool, herein referred as the Integrated Risk Modelling Toolkit (IRMT), to make map-based comparisons showing the effect of different resilient actions on the recovery times. 2. Development of an analytic methodology, referred as the Reconstruction Recovery Model, to estimate post-earthquake recovery 3. Integration of the Reconstruction Recovery Model for practical use into GEM’s OpenQuake modelling platform. 4. Demonstration of reasonable results by using the methodologies to model past earthquakes. In this context, the 2014 M6 South Napa Earthquake was used as a case study. Collaborators Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) Location California, United States
- EU DRR | Global Earthquake Model Foundation
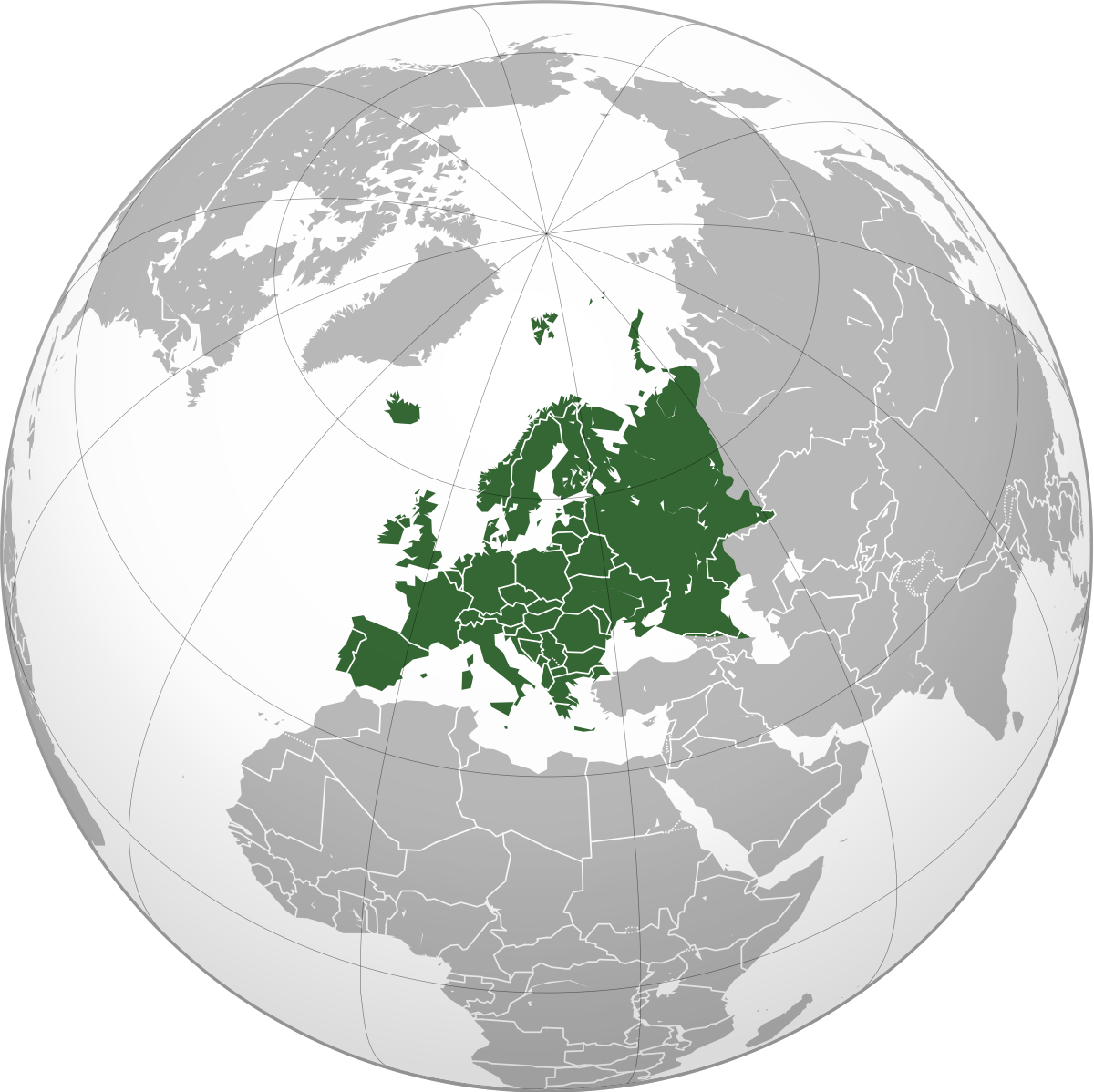
Projects EU DRR Regional risk modelling and scenario analysis for EU Member States - Seismic risk analysis and exposure data Versión en español English version Share Facebook X (Twitter) LinkedIn Overview Background This project supports the World Bank Technical Assistance project "Economic Analysis of Prevention and Preparedness in European Union Member States and Countries under EU Civil Protection Mechanism". The GEM Risk Team provides exposure and probabilistic seismic risk assessments for the 27 EU member states and 6 participating states, building upon the EFEHR ESHM20 hazard and ESRM20 exposure datasets [insert link www.efehr.org ], adding educational and healthcare building stock, and forecasting exposure to 2050. Further, retrofitted vulnerability curves are derived to inform the seismic impact analyses and a cost-benefit analysis. Duration: 2020-2021 Objectives The project is conducted in collaboration with the European Commission’s (EC) Directorate-General for European Civil Protection and Humanitarian Aid Operations (DG ECHO). The objectives of this project are to: 1. Provide regionally-consistent probabilistic seismic risk metrics across Union Civil Protection Mechanism (UCPM) countries for population and selected structure types, to inform macro-economic analysis that is to be conducted by the World Bank project team. 2. Provide seismic impact analysis for two selected earthquake scenarios with and without specified DRM intervention, to estimate the impact of that intervention on i) loss due to direct damage and ii) fatalities. This will contribute to cost-benefit analysis of EU-funded DRM investments conducted by the WB project team using the Triple-Dividend framework. Collaborators GEM Foundation Funding partner: World Bank Group Locations EU Member States
- GEOINQUIRE | Global Earthquake Model Foundation
Projects GEOINQUIRE GeoINQUIRE: Geosphere INfrastructures for QUestions into Integrated REsearch Versión en español English version Share Facebook X (Twitter) LinkedIn Overview Background The GeoINQUIRE project provides and enhances access to selected key data, products, and services, enabling the dynamic processes within the geosphere to be monitored and modelled at new levels of spatial and temporal detail and precision. Geo-INQUIRE benefits from a unique partnership of 51 partners consisting of major national research institutes, universities, national geological surveys, and European consortia. Geo-INQUIRE will enhance and make interoperable the activities of the involved partners and conduct dedicated training programs for their optimal use. A portfolio of 150 Virtual Access (VA) and Transnational Access (TA, both virtual and on-site) installations will be offered to the scientific community. The GEM Foundation is offering one of the Virtual Access services within the geohazard-and-multi-risk-assessment portfolio of services; this service will provide access to earthquake and secondary hazards impact data. Duration: 2022 - 2026 Objectives The project aims to overcome cross-domain barriers, especially the land-sea-atmosphere environments, and will exploit innovative data management techniques, modelling and simulations methods, developments in AI and big data, and extend existing data infrastructures to disseminate these resources to the wider scientific community, including the EOSC landscape. Collaborators Please refer to: https://www.geo-inquire.eu/about/partners Funding partner: European Commission Location Potsdam, Germany
- METIS | Global Earthquake Model Foundation
Projects METIS Methods and Tools Innovation for Seismic Risk Assessment Versión en español English version Share Facebook X (Twitter) LinkedIn Overview Outcomes Training Outreach Photos Publications Background GEM is set to start a 3-year project called METIS or Methods and Tools Innovation for Seismic Risk Assessment funded by the European Commission. The project is part of the Safety margins determination for design basis-exceeding external hazards program. Electricite De France (EDF), a GEM technical collaborator, is coordinating the project which will be implemented in collaboration with 14 other organizations. GEM will contribute to the task on seismic hazard assessment and on PSA Tools and Methodology. In the hazard task, GEM will implement into the OQ Engine methods such as vector-valued probabilistic seismic hazard analysis (PSHA), cluster-based PSHA as well as new methods to propagate epistemic uncertainties. Research will also be carried out in the context of processing earthquake catalogues to remove aftershocks and foreshocks and on testing PSHA models. GEM’s contribution to the PSA Tools and Methodology will concentrate on testing risk results. Objectives The objective of METIS is to translate research into practice through rigorous and efficient methodologies and tools to assess seismic safety of NPP (nuclear power plants). It also aims to innovate current practice by combining simulation with experimental data. The research will develop methods to improve the ability to define safety limits for extremely rare events, which go beyond current design analyses (i.e. design extension for earthquakes). The refined seismic PSA (probabilistic safety assessment) is expected to provide meaningful support in defining regulations for safe design of NPP, as well as for assessing plant safety in real-time in case of temporary unavailability of relevant safety equipment or structures. Collaborators Edf Energy R&D UK Centre Limited - United Kingdom Limited Liability Company Energorisk - Ukraine Helmholtz Zentrum Potsdam Deutschesgeoforschungszentrum Gfz - Germany Geodynamique Et Structure - France Institut De Radioprotection Et De Surete Nucleaire - France Istituto Universitario Di Studi Superiori Di Pavia - Italy Lgi Consulting - France National Technical University of Athens – NTUA - Greece State Enterprise State Scientific and Technical Center For Nuclear And Radiation Safety - Ukraine Technische Universitat Kaiserslautern - Germany Univerza V Ljubljani - Slovenia Geo-Research Institute - Japan North Carolina State University - United States The Regents of The University Of California - United States Location Europe Horizon 2020 METIS Project fact sheet EdF and GEM METIS project collaboration from 2020 to 2024. New Horizon 2020 project launched to develop an advanced approach for Seismic Risk Assessment of Nuclear Power Plants
- SOLOMON ISLANDS EXPOSURE | Global Earthquake Model Foundation
Projects SOLOMON ISLANDS EXPOSURE Assessing the Risk Exposure of Road Network to Climate and Natural Hazard Risks in Solomon Islands Versión en español English version Share Facebook X (Twitter) LinkedIn Overview Background This project aims to conduct a robust multi-hazard risk assessment of the road network to climate and natural hazards in the Solomon Islands, both historically and under future climate projections. The project includes three main dimensions: - Characterization of the climate and natural hazards - Physical vulnerability of the road network - Multi-criteria criticality analysis The three main outputs are: - Multi-hazard maps - Road network risk exposure analysis (global risk score) - Identification of "first priority" road segments and estimation of their rehabilitation costs The GEM Hazard Team supports the project by computing seismic hazard maps and uses these to produce maps to classify low to high risks of earthquake hazards, according to their intensity and frequency. Duration: 2021 Objectives Many Small Island Developing States (SIDS) share a major common feature: they are among the most exposed nations to natural hazards and climate change. SIDS are also characterized by insularity and geographic remoteness, as well as small geographic area, economies, and population, all of which increase their social and economic vulnerability. This project aims to assist the Solomon Islands to better manage climate and disaster risks by improving the understanding of risk and the use of this information for risk reduction decision-making, and the design and implementation of investments at the provincial and community level. Collaborators GEM Foundation, ARIA Technologies, Actimar, Suez Consulting, Setec Group Funding partner: World Bank Group Location Solomon Islands
- ARISTOTLE | Global Earthquake Model Foundation
Projects ARISTOTLE Multi-Hazard Expert Advice System for ERCC Versión en español English version Share Facebook X (Twitter) LinkedIn Overview Background The ARISTOTLE consortium combines a number of services that enable a rapid understanding of events from various natural hazards (earthquakes and tsunami, volcanoes, severe weather and floods) and how they might unfold, thus aiding a deeper interpretation of the resulting hazards and impact. The GEM Foundation is supporting the consortium by providing an assessment of the impact of earthquakes using GEM's global exposure and vulnerability models, with a focus on metrics such as collapsed buildings and displaced people, such that it may provide an added value to existing rapid loss assessment services such as the USGS's Prompt Assessment of Global Earthquakes for Response (PAGER). Duration: 2022 - 2024 Objectives ARISTOTLE aims to provide Multi-Hazard Advice to the European Research Coordination Centre, either in advance of / during the activation of the EC Civil Protection Mechanism (CPM), in order to increase preparedness and response levels of the EU and to improve the ERCC’s assessment capacity. Collaborators ARISTOTLE is a multi-disciplinary partnership consisting of world-leading scientific centres in the areas of Earth and Climate sciences, providing operational and monitoring services, early warning and information systems as well as contributing to innovation and research actions. Location Global (Rome, Italy)